
1. What is EHI? The Energy Helicity Index (EHI) is a combination of two indexes. By itself, it is the best index available for tornado prediction since it combines both CAPE and Helicity. The CAPE is the amount of pure instability present from a parcel of air that rises from the lower PBL. Helicity is the product of low level shearing (known as streamwise vorticity) and storm inflow directly into the streamwise vorticity. The Helicity is storm relative which means the Helicity is calculated from the storm's frame of reference. 2. How is EHI determined?: EHI = (CAPE * SR HEL) / 160,000 The sounding at the bottom shows an EHI value of about 6. The EHI value has no units. Here is how the value was determine: CAPE = 4,385 J/kg SR HEL = 220 m^2/s^2 EHI = (4,385 * 220) / 160,000 = 6 3. Operational significance of EHI:
4. Pitfalls: a. Tornadoes are still possible in cases with a low EHI in cases where the CAPE or the shear is very large. This is especially true when the CAPE is low based and when mesoscale boundaries enhance the Helicity. b. HEL is especially variable on the mesoscale-- thus EHI may be much higher in particular areas. c. Make sure storms will develop in the first place in the high EHI environment (i.e. cap will break). 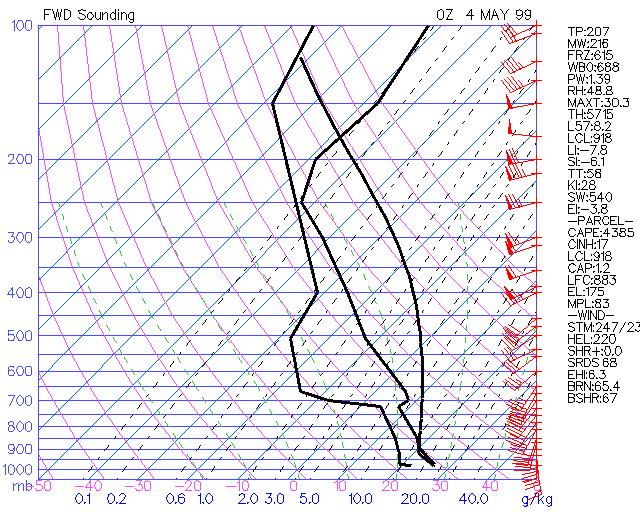 |