
1. What is EI? EI (Energy Index) is an index for assessing the severe storm potential by comparing the heat and moisture characteristics between the low level (850 mb) and middle level environment (500 mb). An environment that is warm and moist in the low levels and cool and dry in the middle levels is convectively unstable. 2. How is EI determined?  cp= specific heat for dry air at constant pressure (1,004 JK^-1kg^-1)) T= temperature at pressure level (found on sounding, units of K) g= gravity (9.8 ms^-2) Z= geopotential height (found on sounding, m) L= latent heat of vaporization (~2,400,000 Jkg^-1) w= mixing ratio (found on sounding, kg/kg) The sounding at the bottom has an EI of -3.8 C 3. Operational significance of EI:
4. Pitfalls: a. Cap must break for the EI value to have significance. 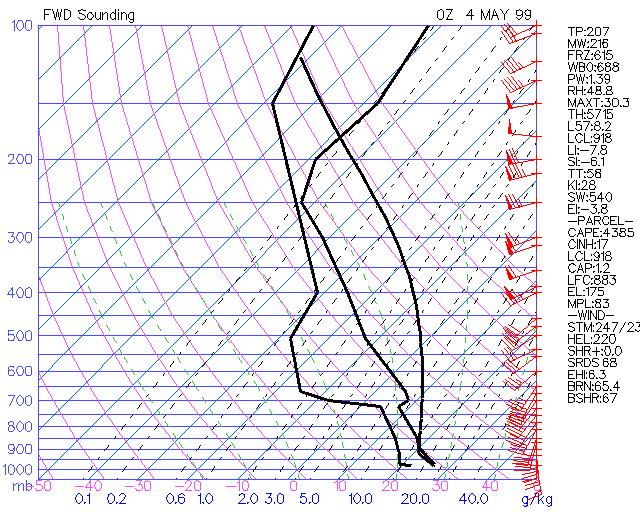
|