
Bright banding occurs due to the higher reflectivities associated with snow that is melting as it is falling aloft. Ice is a better absorber of radar radiation compared to liquid water. Because of this, snow will show a lower reflectivity on radar when it has the same moisture content as a rain event. When the snow is melting however, a film of water forms on the outside of the snowflake. Since snowflakes can be fairly large, when there is a film of water on the snowflake it has the same reflectivity as a a giant raindrop or small wet hail. A radar beam will generally sample a higher elevation as it moves away from the radar site. Because the melting of the snowflakes occurs within a specific elevation range aloft, there will be a higher reflectivity as the radar beam moves through this layer. This can produce a circular or arcing band of higher reflectivity around the radar site on the reflectivity display. Below are some bright banding examples (more examples will be added over time): Dallas / Ft. Worth Area Bright Band 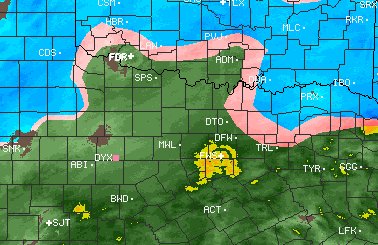
|